Many individuals may not recognize its significance or know how to interpret it within the context of their investment decisions. Book value per share is a critical measure that savvy investors incorporate when concocting an effective investment strategy. One such strategy is value investing, where investors use book value per share to assess the intrinsic value of a company’s equity. If the company’s book value unearned revenue benefits, examples, accounting and reporting is consistently decreasing, it’s often a red flag that the company’s liabilities are increasing, or its assets are deteriorating. In reality, during the liquidation of a company, the actual amount received per share may be more or less than this figure due to various factors such as market conditions or legal issues. The calculation of the book value per share is a relatively simple, straightforward process.
Why Does BVPS Matter in Investing?
In the example from a moment ago, a company has $1,000,000 in equity and 1,000,000 shares outstanding. Now, let’s say that the company invests in a new piece of equipment that costs $500,000. The book value per share would still be $1 even though the company’s assets have increased in value. BVPS represents the accounting value of each share based on the company’s equity, while the market value per share is determined by the stock’s current trading price in the market. By representing the net asset value per share, it allows investors to assess the portion of assets allocated to each outstanding share.
Reflects the Company’s Financial Health

It’s important to note that the company’s stock is valued in the books of accounts based on its historical cost, not its current market value. In conclusion, book value is a fundamental metric that provides valuable insights into a company’s net asset value per share. Investors searching for undervalued stocks will typically look for businesses where the book value per share is higher than the current market price of a share. This is what is generally referred to as ‘trading below book value’, signifying that the market may be underestimating the worth of the company’s assets. On the other hand, the market value per share, also known as share price, is the price that the stock is currently trading at in the market. It reflects what investors are willing to pay for a share of the company right now.
Using Book Value in Investment Analysis
It provides insights into the net asset value of a company and can assist in making informed investment decisions. For instance, consider a company’s brand value, which is built through a series of marketing campaigns. U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) require marketing costs to be expensed immediately, reducing the book value per share. However, if advertising efforts enhance the image of a company’s products, the company can charge premium prices and create brand value. Market demand may increase the stock price, which results in a large divergence between the market and book values per share.
Thus, the components of BVPS are tangible assets, intangible assets, and liabilities. When a company has a high book value per share, it may signify its strategic emphasis on sustainability. In the process of M&A, it’s crucial to establish a fair price for the company that is being acquired. The book value per share can assist here by suggesting a baseline for negotiation. If a company’s market value is significantly higher than its book value, it may indicate that the market has high expectations for the firm’s future earnings. Conversely, if the market value is lower, it may be a signal the company is undervalued, or the market anticipates future problems.
- Despite the increase in share price (and market capitalization), the book value of equity per share (BVPS) remained unchanged in Year 1 and 2.
- When evaluating a company’s financial health, investors and analysts often rely on various financial ratios and metrics.
- If we assume the company has preferred equity of $3mm and a weighted average share count of 4mm, the BVPS is $3.00 (calculated as $15mm less $3mm, divided by 4mm shares).
- For these kinds of businesses, the book value per share can provide a fairly accurate value of the company’s actual worth, as their assets can be readily evaluated and have a definite resale value.
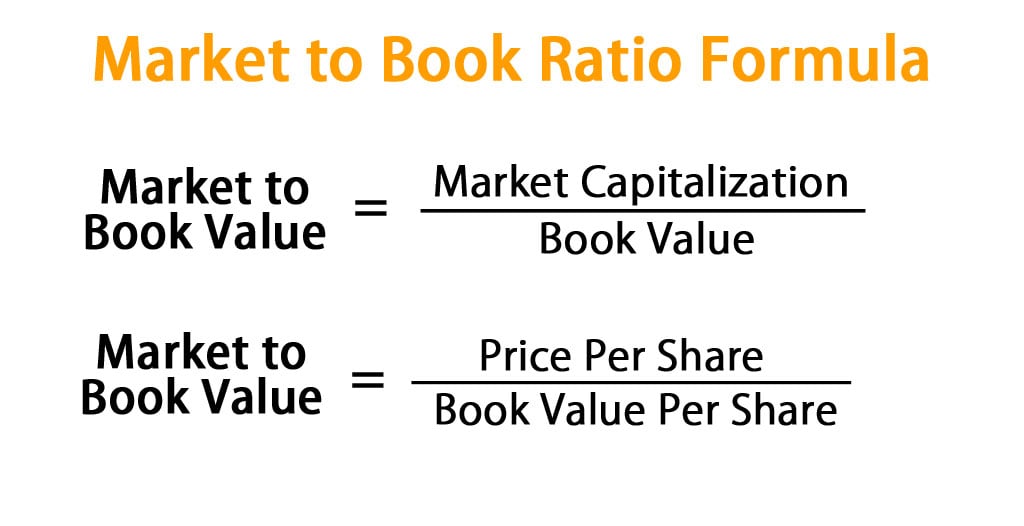
What Does a Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio of 1.0 Mean?
Google, for instance, has an extensive portfolio of intangible assets like its search engine algorithms, customer data, and globally recognized brand, all of which are not reflected in its book value. Therefore, the BVPS for Google will likely undervalue the company if it does not account for these assets. Book value per share holds a significant relationship to a company’s commitment to Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and sustainability. It can serve as a key metric to assess a company’s reliable performance in these areas.
When compared with the market price, the book value of a stock assists investors in identifying potential investment prospects. Book value per share (BVPS) is a measure of value of a company’s common share based on book value of the shareholders’ equity of the company. It is the amount that shareholders would receive if the company dissolves, realizes cash equal to the book value of its assets and pays liabilities at their book value. Dividends are portions of a corporation’s profit paid out to shareholders, and their declaration and payment can affect the book value per share. If a company pays dividends from its profits or retained earnings, it will decrease the retained earnings in the shareholder’s equity part of the balance sheet, resulting in a lower book value.
However, for sectors like technology and pharmaceuticals, where intellectual property and ongoing research and development are crucial, BVPS can be misleading. Clear differences between the book value and market value of equity can occur, which happens more often than not for the vast majority of companies. With those three assumptions, we can calculate the book value of equity as $1.6bn. Alternatively, another method to increase the BVPS is via share repurchases (i.e. buybacks) from existing shareholders. If relevant, the value of preferred equity claims should also be subtracted from the numerator, the book value of equity. In conclusion, book value per share can hold meaningful implications for a company’s commitment to CSR and sustainability.
As a company’s potential profitability, or its expected growth rate, increases, the corresponding market value per share will also increase. A company can use a portion of its earnings to buy assets that would increase common equity along with BVPS. Or, it could use its earnings to reduce liabilities, which would also increase its common equity and BVPS. A company’s stock is considered undervalued when BVPS is higher than a company’s market value or current stock price. If the BVPS increases, the stock is perceived as more valuable, and the price should increase.
